迪杰斯特拉算法
提示
- 算法基本原理:迪杰斯特拉算法通过贪心方法,从起点开始逐渐扩展到其他所有顶点,寻找最短路径。
- 关键特性:算法中任何子路径也是两点间的最短路径,用于逐步更新顶点的最短距离。
- 应用场景:广泛应用于计算图中两点间的最短路径,如地图导航、社交网络和电话网络等。
它与最小生成树不同,因为两个顶点之间的最短距离可能不包括图中的所有顶点。
Dijkstra 算法的工作原理
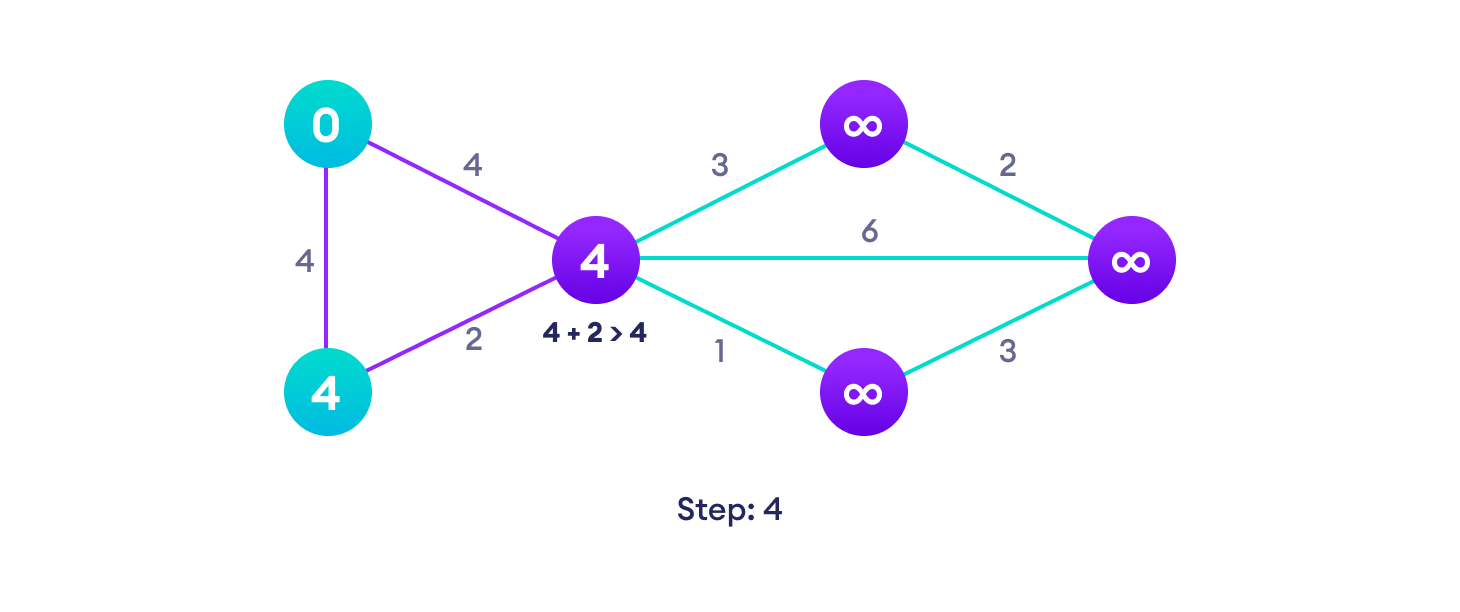
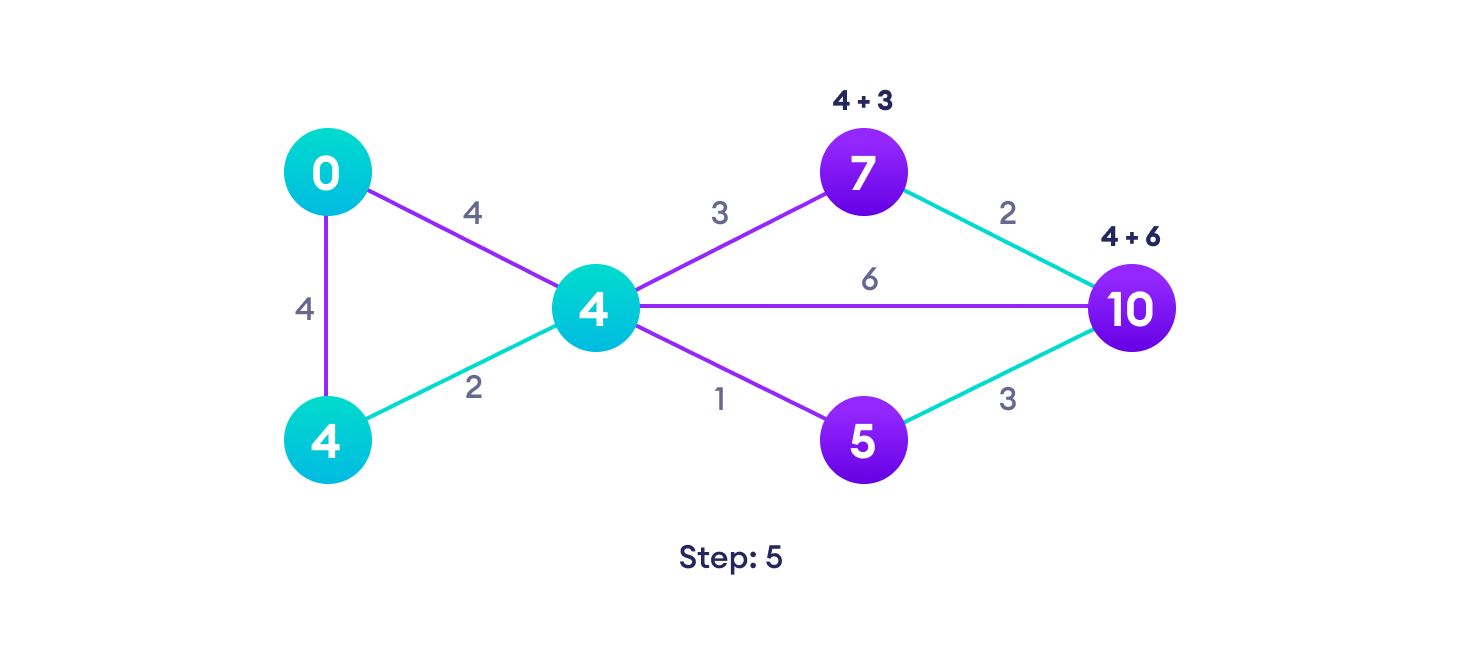
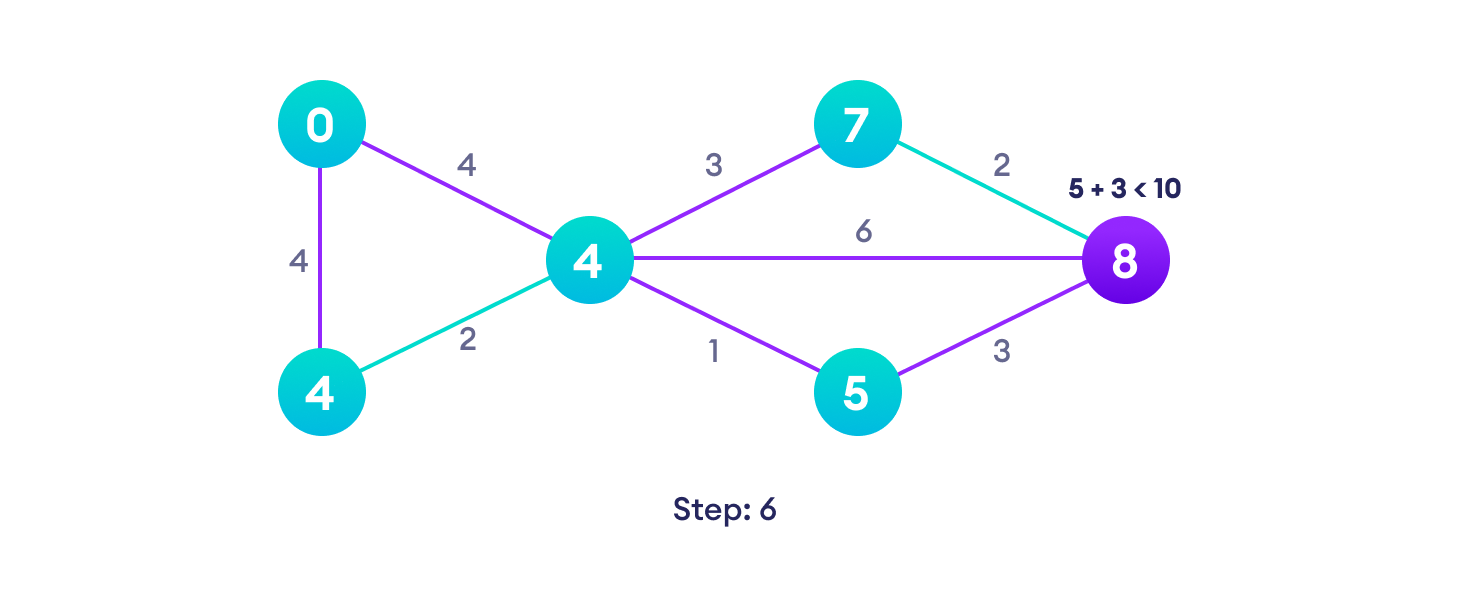
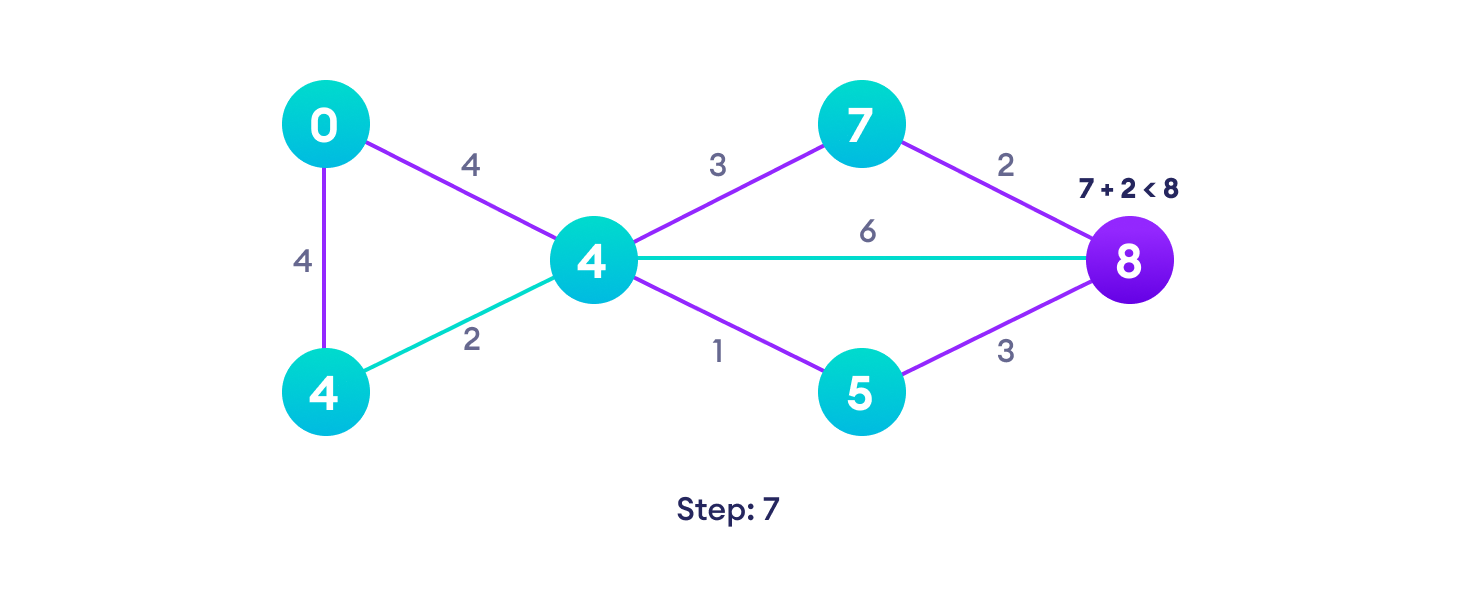
Dijkstra 算法基于这样一个原理:最短路径 A -> D 中的任何子路径 B -> D 也是顶点 B 和 D 之间的最短路径。
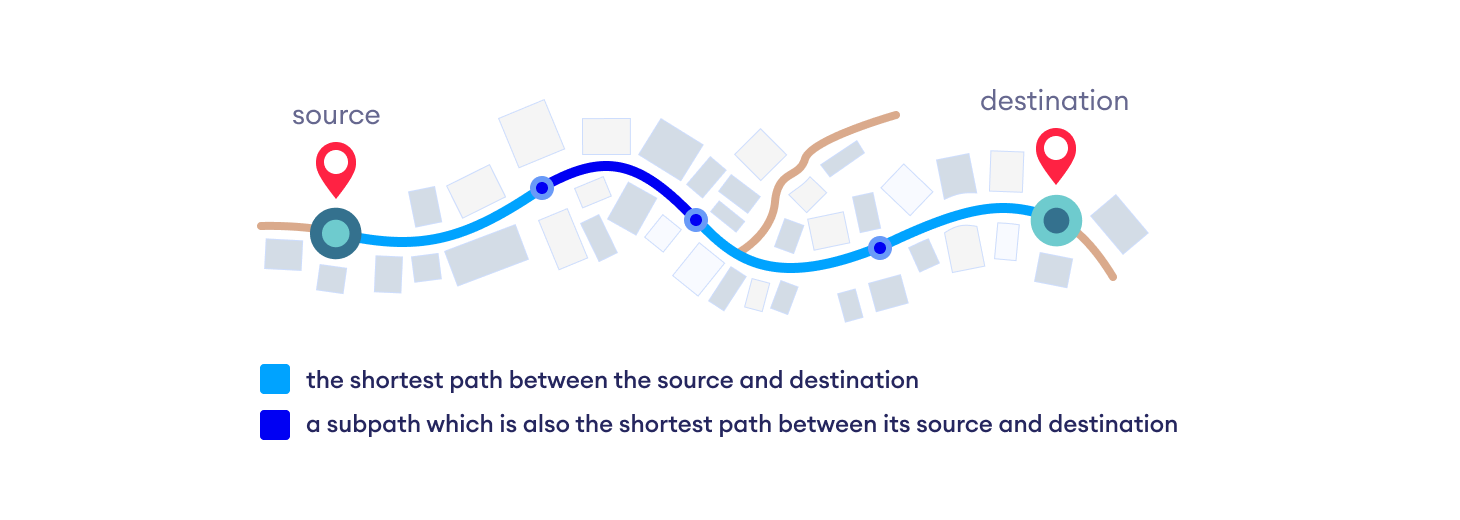
Dijkstra 使用这一属性的反方向,即我们高估了每个顶点从起始顶点的距离。然后我们访问每个节点及其邻居,以找到通往这些邻居的最短子路径。
该算法采用贪心方法,即我们寻找下一个最佳解决方案,希望最终结果是整个问题的最佳解决方案。
Dijkstra 算法示例
从一个例子开始,然后再考虑算法是更容易的。
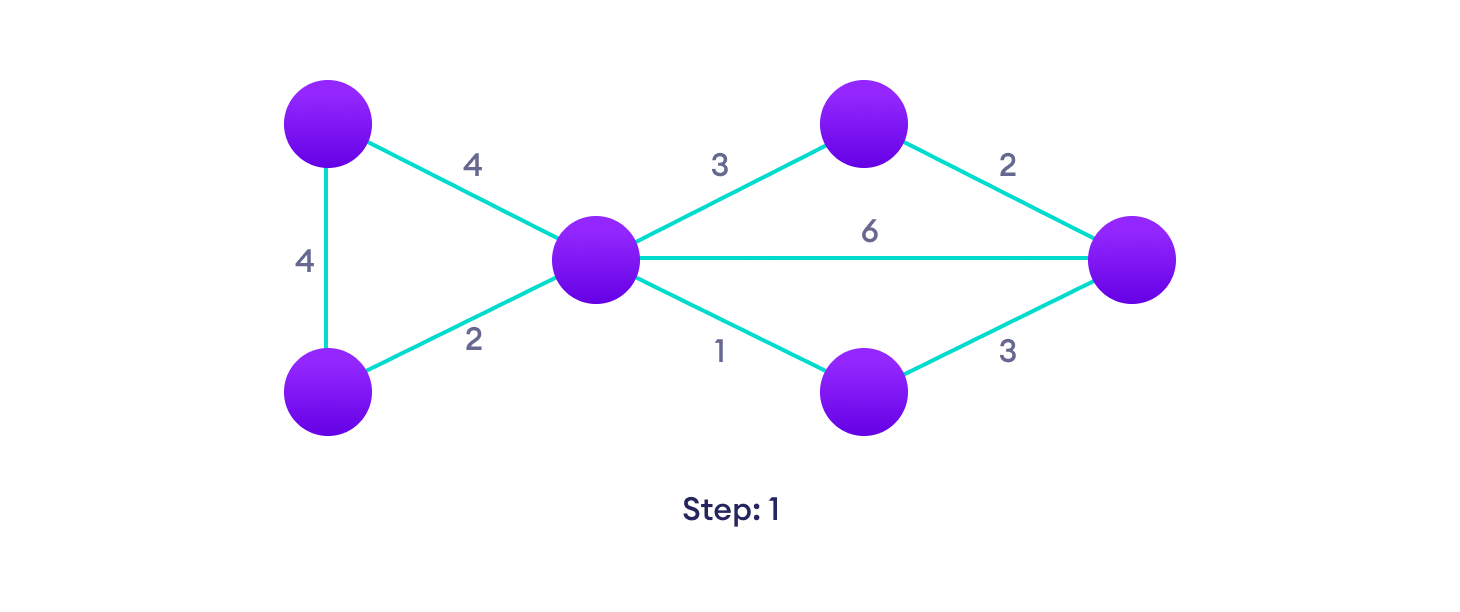
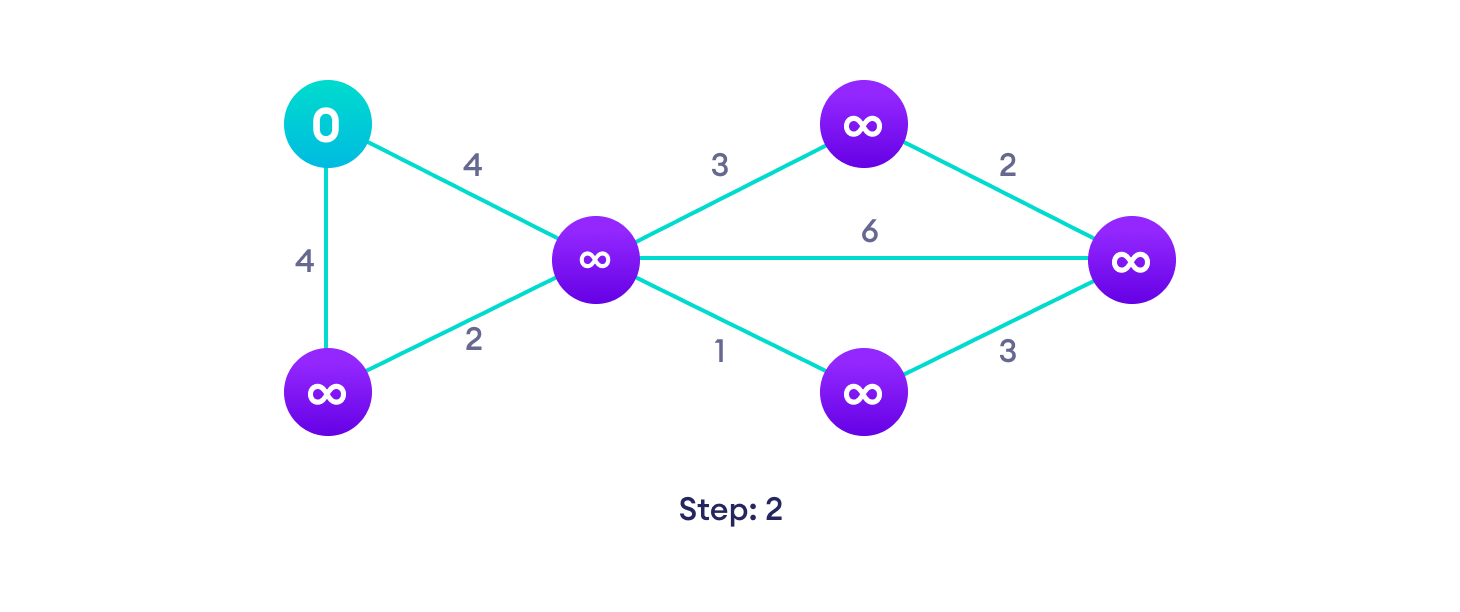
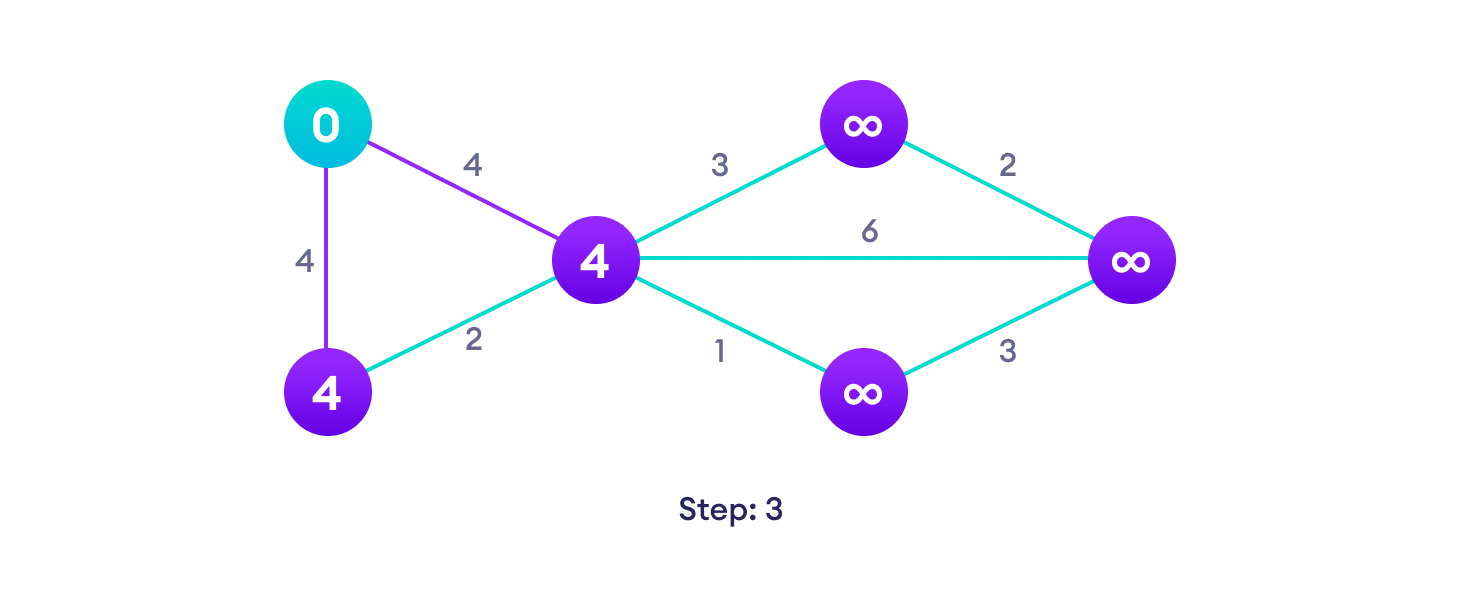
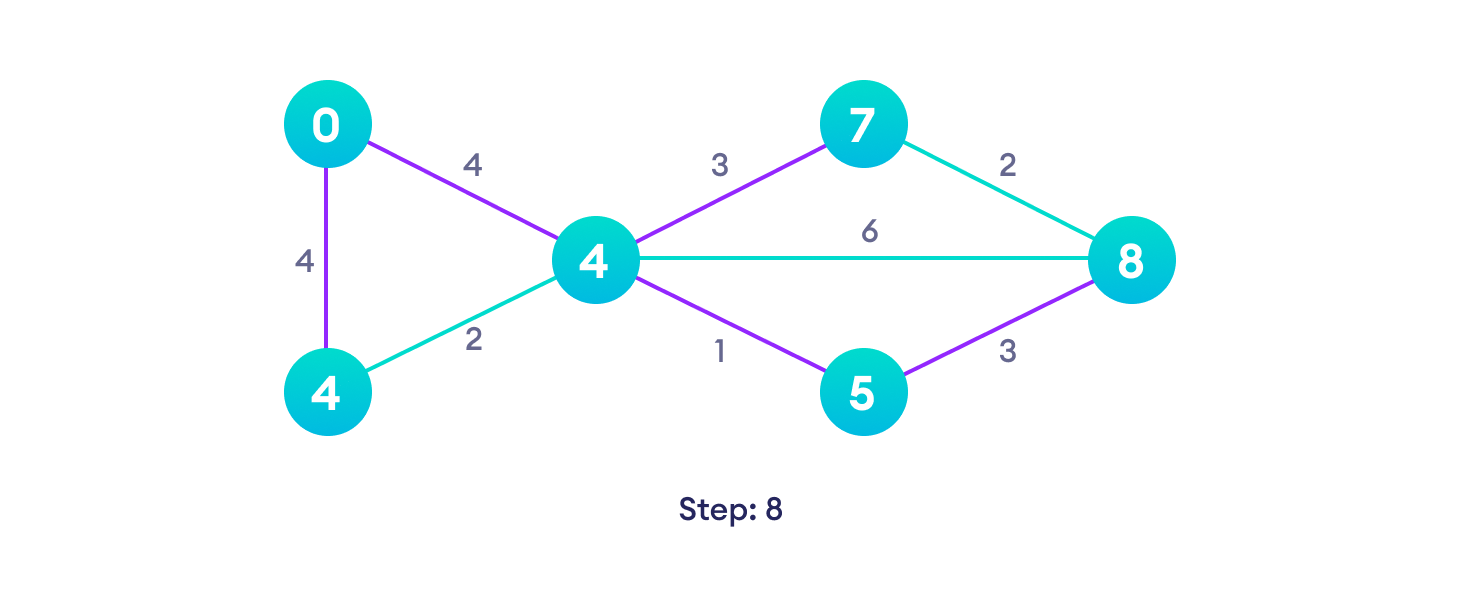
Dijkstra 算法伪代码
我们需要维护每个顶点的路径距离。我们可以在一个大小为 v 的数组中存储它,其中 v 是顶点的数量。
我们还想能够获得最短路径,而不仅仅是知道最短路径的长度。为此,我们将每个顶点映射到最后更新其路径长度的顶点。
算法结束后,我们可以从目的地顶点回溯到源顶点以找到路径。
可以使用最小优先队列有效地接收最短路径距离的顶点。
function dijkstra(G, S)
for each vertex V in G
distance[V] <- infinite
previous[V] <- NULL
If V != S, add V to Priority Queue Q
distance[S] <- 0
while Q IS NOT EMPTY
U <- Extract MIN from Q
for each unvisited neighbour V of U
tempDistance <- distance[U] + edge_weight(U, V)
if tempDistance < distance[V]
distance[V] <- tempDistance
previous[V] <- U
return distance[], previous[]
Dijkstra 算法的代码
Dijkstra 算法在 C++ 中的实现如下。该代码的复杂性可以改进,但抽象是便于将代码与算法联系起来的。
# Python 中的Dijkstra 算法
import sys
# 提供图
vertices = [[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]]
edges = [[0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 3, 0],
[1, 2, 0, 1, 3, 0, 0],
[2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]]
# Find which vertex is to be visited next
def to_be_visited():
global visited_and_distance
v = -10
for index in range(num_of_vertices):
if visited_and_distance[index][0] == 0 \
and (v < 0 or visited_and_distance[index][1] <=
visited_and_distance[v][1]):
v = index
return v
num_of_vertices = len(vertices[0])
visited_and_distance = [[0, 0]]
for i in range(num_of_vertices-1):
visited_and_distance.append([0, sys.maxsize])
for vertex in range(num_of_vertices):
# Find next vertex to be visited
to_visit = to_be_visited()
for neighbor_index in range(num_of_vertices):
# Updating new distances
if vertices[to_visit][neighbor_index] == 1 and \
visited_and_distance[neighbor_index][0] == 0:
new_distance = visited_and_distance[to_visit][1] \
+ edges[to_visit][neighbor_index]
if visited_and_distance[neighbor_index][1] > new_distance:
visited_and_distance[neighbor_index][1] = new_distance
visited_and_distance[to_visit][0] = 1
i = 0
# Printing the distance
for distance in visited_and_distance:
print("Distance of ", chr(ord('a') + i),
" from source vertex: ", distance[1])
i = i + 1
// Java 中的 Dijkstra 算法
public class Dijkstra {
public static void dijkstra(int[][] graph, int source) {
int count = graph.length;
boolean[] visitedVertex = new boolean[count];
int[] distance = new int[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
visitedVertex[i] = false;
distance[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// 自环的距离为零
distance[source] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 更新邻接顶点和源顶点之间的距离
int u = findMinDistance(distance, visitedVertex);
visitedVertex[u] = true;
// 更新所有邻接顶点的距离
for (int v = 0; v < count; v++) {
if (!visitedVertex[v] && graph[u][v] != 0 && (distance[u] + graph[u][v] < distance[v])) {
distance[v] = distance[u] + graph[u][v];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < distance.length; i++) {
System.out.println(String.format("从 %s 到 %s 的距离是 %s", source, i, distance[i]));
}
}
// 查找最小距离
private static int findMinDistance(int[] distance, boolean[] visitedVertex) {
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int minDistanceVertex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < distance.length; i++) {
if (!visitedVertex[i] && distance[i] < minDistance) {
minDistance = distance[i];
minDistanceVertex = i;
}
}
return minDistanceVertex;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int graph[][] = new int[][] { { 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 3, 0 }, { 1, 2, 0, 1, 3, 0, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 }, { 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0 }, { 0, 3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1 }, { 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 } };
Dijkstra T = new Dijkstra();
T.dijkstra(graph, 0);
}
}
// C 中的 Dijkstra 算法
#include <stdio.h>
#define INFINITY 9999
#define MAX 10
void Dijkstra(int Graph[MAX][MAX], int n, int start);
void Dijkstra(int Graph[MAX][MAX], int n, int start) {
int cost[MAX][MAX], distance[MAX], pred[MAX];
int visited[MAX], count, mindistance, nextnode, i, j;
// 创建成本矩阵
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (Graph[i][j] == 0)
cost[i][j] = INFINITY;
else
cost[i][j] = Graph[i][j];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
distance[i] = cost[start][i];
pred[i] = start;
visited[i] = 0;
}
distance[start] = 0;
visited[start] = 1;
count = 1;
while (count < n - 1) {
mindistance = INFINITY;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (distance[i] < mindistance && !visited[i]) {
mindistance = distance[i];
nextnode = i;
}
visited[nextnode] = 1;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (!visited[i])
if (mindistance + cost[nextnode][i] < distance[i]) {
distance[i] = mindistance + cost[nextnode][i];
pred[i] = nextnode;
}
count++;
}
// 打印距离
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (i != start) {
printf("\n从源点到 %d 的距离为: %d", i, distance[i]);
}
}
int main() {
int Graph[MAX][MAX], i, j, n, u;
n = 7;
Graph[0][0] = 0;
Graph[0][1] = 0;
Graph[0][2] = 1;
Graph[0][3] = 2;
Graph[0][4] = 0;
Graph[0][5] = 0;
Graph[0][6] = 0;
Graph[1][0] = 0;
Graph[1][1] = 0;
Graph[1][2] = 2;
Graph[1][3] = 0;
Graph[1][4] = 0;
Graph[1][5] = 3;
Graph[1][6] = 0;
Graph[2][0] = 1;
Graph[2][1] = 2;
Graph[2][2] = 0;
Graph[2][3] = 1;
Graph[2][4] = 3;
Graph[2][5] = 0;
Graph[2][6] = 0;
Graph[3][0] = 2;
Graph[3][1] = 0;
Graph[3][2] = 1;
Graph[3][3] = 0;
Graph[3][4] = 0;
Graph[3][5] = 0;
Graph[3][6] = 1;
Graph[4][0] = 0;
Graph[4][1] = 0;
Graph[4][2] = 3;
Graph[4][3] = 0;
Graph[4][4] = 0;
Graph[4][5] = 2;
Graph[4][6] = 0;
Graph[5][0] = 0;
Graph[5][1] = 3;
Graph[5][2] = 0;
Graph[5][3] = 0;
Graph[5][4] = 2;
Graph[5][5] = 0;
Graph[5][6] = 1;
Graph[6][0] = 0;
Graph[6][1] = 0;
Graph[6][2] = 0;
Graph[6][3] = 1;
Graph[6][4] = 0;
Graph[6][5] = 1;
Graph[6][6] = 0;
u = 0;
Dijkstra(Graph, n, u);
return 0;
}
// Dijkstra 算法在 C++ 中的实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define INT_MAX 10000000
using namespace std;
void DijkstrasTest();
int main() {
DijkstrasTest();
return 0;
}
class Node;
class Edge;
void Dijkstras();
vector<Node*>* AdjacentRemainingNodes(Node* node);
Node* ExtractSmallest(vector<Node*>& nodes);
int Distance(Node* node1, Node* node2);
bool Contains(vector<Node*>& nodes, Node* node);
void PrintShortestRouteTo(Node* destination);
vector<Node*> nodes;
vector<Edge*> edges;
class Node {
public:
Node(char id)
: id(id), previous(NULL), distanceFromStart(INT_MAX) {
nodes.push_back(this);
}
public:
char id;
Node* previous;
int distanceFromStart;
};
class Edge {
public:
Edge(Node* node1, Node* node2, int distance)
: node1(node1), node2(node2), distance(distance) {
edges.push_back(this);
}
bool Connects(Node* node1, Node* node2) {
return (
(node1 == this->node1 &&
node2 == this->node2) ||
(node1 == this->node2 &&
node2 == this->node1));
}
public:
Node* node1;
Node* node2;
int distance;
};
///////////////////
void DijkstrasTest() {
Node* a = new Node('a');
Node* b = new Node('b');
Node* c = new Node('c');
Node* d = new Node('d');
Node* e = new Node('e');
Node* f = new Node('f');
Node* g = new Node('g');
Edge* e1 = new Edge(a, c, 1);
Edge* e2 = new Edge(a, d, 2);
Edge* e3 = new Edge(b, c, 2);
Edge* e4 = new Edge(c, d, 1);
Edge* e5 = new Edge(b, f, 3);
Edge* e6 = new Edge(c, e, 3);
Edge* e7 = new Edge(e, f, 2);
Edge* e8 = new Edge(d, g, 1);
Edge* e9 = new Edge(g, f, 1);
a->distanceFromStart = 0; // 设置起始节点
Dijkstras();
PrintShortestRouteTo(f);
}
///////////////////
void Dijkstras() {
while (nodes.size() > 0) {
Node* smallest = ExtractSmallest(nodes);
vector<Node*>* adjacentNodes =
AdjacentRemainingNodes(smallest);
const int size = adjacentNodes->size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Node* adjacent = adjacentNodes->at(i);
int distance = Distance(smallest, adjacent) +
smallest->distanceFromStart;
if (distance < adjacent->distanceFromStart) {
adjacent->distanceFromStart = distance;
adjacent->previous = smallest;
}
}
delete adjacentNodes;
}
}
// 查找具有最小距离的节点,
// 将其移除并返回。
Node* ExtractSmallest(vector<Node*>& nodes) {
int size = nodes.size();
if (size == 0) return NULL;
int smallestPosition = 0;
Node* smallest = nodes.at(0);
for (int i = 1; i < size; ++i) {
Node* current = nodes.at(i);
if (current->distanceFromStart <
smallest->distanceFromStart) {
smallest = current;
smallestPosition = i;
}
}
nodes.erase(nodes.begin() + smallestPosition);
return smallest;
}
// 返回所有仍在 'nodes' 集合中的
// 与 'node' 相邻的节点。
vector<Node*>* AdjacentRemainingNodes(Node* node) {
vector<Node*>* adjacentNodes = new vector<Node*>();
const int size = edges.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Edge* edge = edges.at(i);
Node* adjacent = NULL;
if (edge->node1 == node) {
adjacent = edge->node2;
} else if (edge->node2 == node) {
adjacent = edge->node1;
}
if (adjacent && Contains(nodes, adjacent)) {
adjacentNodes->push_back(adjacent);
}
}
return adjacentNodes;
}
// 返回两个相连节点之间的距离
int Distance(Node* node1, Node* node2) {
const int size = edges.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Edge* edge = edges.at(i);
if (edge->Connects(node1, node2)) {
return edge->distance;
}
}
return -1; // 永远不应发生
}
// 'nodes' 向量是否包含 'node'
bool Contains(vector<Node*>& nodes, Node* node) {
const int size = nodes.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if (node == nodes.at(i)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
///////////////////
void PrintShortestRouteTo(Node* destination) {
Node* previous = destination;
cout << "从起点到此的距离: "
<< destination->distanceFromStart << endl;
while (previous) {
cout << previous->id << " ";
previous = previous->previous;
}
cout << endl;
}
// 这两个不需要
vector<Edge*>* AdjacentEdges(vector<Edge*>& Edges, Node* node);
void RemoveEdge(vector<Edge*>& Edges, Edge* edge);
vector<Edge*>* AdjacentEdges(vector<Edge*>& edges, Node* node) {
vector<Edge*>* adjacentEdges = new vector<Edge*>();
const int size = edges.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
Edge* edge = edges.at(i);
if (edge->node1 == node) {
cout << "相邻: " << edge->node2->id << endl;
adjacentEdges->push_back(edge);
} else if (edge->node2 == node) {
cout << "相邻: " << edge->node1->id << endl;
adjacentEdges->push_back(edge);
}
}
return adjacentEdges;
}
void RemoveEdge(vector<Edge*>& edges, Edge* edge) {
vector<Edge*>::iterator it;
for (it = edges.begin(); it < edges.end(); ++it) {
if (*it == edge) {
edges.erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
Dijkstra 算法的复杂度
时间复杂度:O(E Log V)
其中,E 是边的数量,V 是顶点的数量。
空间复杂度:O(V)
Dijkstra 算法的应用
- 寻找最短路径
- 在社交网络应用中
- 在电话网络中
- 在地图上寻找位置